What is Arthritis?
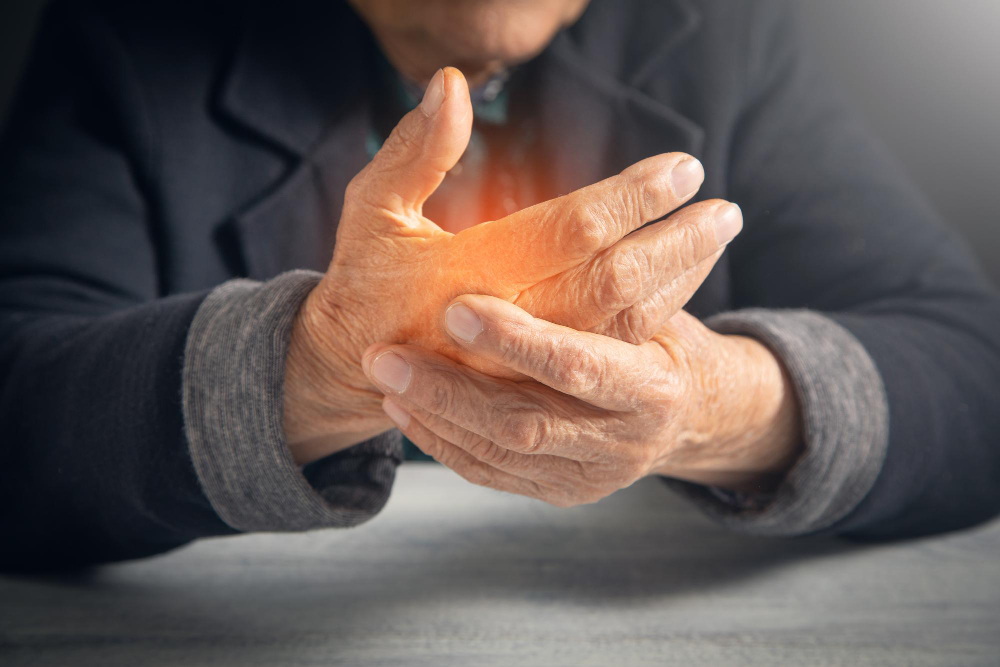
Arthritis is a common condition that affects the joints. It causes pain, swelling, and stiffness. Many people think arthritis only affects older adults. However, it can happen at any age. There are over 100 types of arthritis. The most common types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis happens when the cartilage in joints wears down. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This means the body’s immune system attacks the joints by mistake. According to the CDC, arthritis is a leading cause of disability worldwide. Early treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
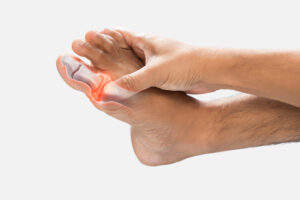
Common Symptoms of Arthritis
Arthritis symptoms can vary from person to person. Yet, some signs are very common. Recognizing these early can help you seek treatment sooner. For example, you may notice:
Sometimes, symptoms come and go. But over time, they may get worse if not treated. If you notice these signs, it is important to talk to a doctor.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are many causes of arthritis. Some types, like osteoarthritis, happen due to wear and tear on the joints. Others, like rheumatoid arthritis, are caused by the immune system attacking the joints. In addition, certain factors can increase your risk:
Knowing your risk factors can help you take steps to protect your joints.
Diagnosis Methods
Doctors use several methods to diagnose arthritis. First, they will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they will examine your joints for swelling, redness, and movement. Sometimes, tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis. These may include:
Early diagnosis is important. It helps start treatment sooner and may prevent further joint damage.
Treatment Options
Treatment for arthritis aims to reduce pain and improve joint function. There are several options available. Your doctor will suggest the best plan for you. Common treatments include:
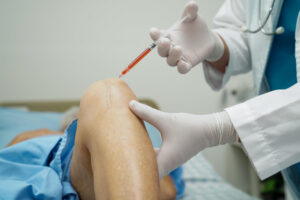
Medical Treatments
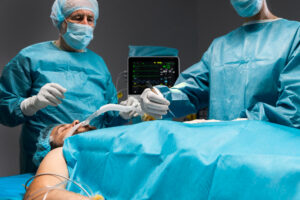
Surgical Treatments
Lifestyle Changes
With the right treatment, many people manage arthritis well and stay active.
Prevention Tips and Lifestyle Guidance
While not all types of arthritis can be prevented, you can lower your risk. Simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference. For instance:
By following these tips, you can help protect your joints and improve your overall health.
For more information, you can visit trusted sources like the CDC and the WHO.
Consult an orthopedic specialist for personalized advice about arthritis.